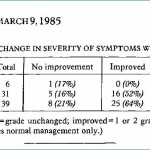
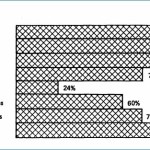
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 71: 391-397. NOTE: This is not actually a study of Red 3. Rather, the dye, Red 3, is to help develop this testing method, because it is a known excitatory neurotoxin. The relative refractory period is … Continue reading